Upcoming Events
17 Sep 2024
Second Research Methodology Workshop on Widening Access to Higher Education in India: Institutional Approaches to be held on 17-18 September, 2024
Recent Events
| Date | Event |
|---|---|
| 28 Aug 2024 | Second Research Advisory Committee Meeting on Widening Access to Higher Education in India: Institutional Approaches to be held on 28 August 2024, New Delhi (Online) |
| 2 Aug 2024 | First Peer Review Meeting on IHER 2025: Multidisciplinary Higher Education on 02 August, 2024 (Online) |
| 6 Mar 2024 | Executive Committee Meeting on March 06, 2024 (Online) |
 The CPRHE is envisaged to act as a think tank in higher education policy and planning in India. The Centre will analyze trends in higher education development; promote research to generate reliable information base for policy and planning; help develop long-term perspective plans at the Centre and state levels; and encourage policy dialogues involving national and state-level education policy makers and develop a network of educational researcher institutions, universities and international institutions and organizations engaged in policy analysis and research in higher education.
The CPRHE is envisaged to act as a think tank in higher education policy and planning in India. The Centre will analyze trends in higher education development; promote research to generate reliable information base for policy and planning; help develop long-term perspective plans at the Centre and state levels; and encourage policy dialogues involving national and state-level education policy makers and develop a network of educational researcher institutions, universities and international institutions and organizations engaged in policy analysis and research in higher education.
The CPRHE is engaged in higher education policy research focusing on the current national priorities in the following inter-related areas: a) expanding and improving the provision of higher education ensuring equity and inclusion; b) enhancing quality; c) improving relevance of study programmes and employability of higher education graduates; d) improving financial efficiency and flows; e) strengthening teaching learning process and improving learning outcomes; and f) increasing efficiency and effectiveness of governance and management.
Based on the research studies the CPRHE will be bringing out research papers, research reports, policy briefs and books and articles in academic journals. These documents will form the basis for organizing policy dialogues, consultation meetings and seminars in an effort to make policy making and planning in the country more evidence based.


CPRHE-RESEARCH
CPRHE has currently six ongoing research projects. The sixth research project on the theme of employability of higher education graduates is in the final stages of development and will soon be implemented. To know more about the ongoing Research Projects, click on the title of the project & follow the link.
Given the diversification of higher education system and the consequent diversity in the student population, this research project aims to explore the diversity and discrimination in the higher education campuses in India. As a result of higher education expansion and enhanced aspiration levels of families cutting across the class and caste boundaries, campuses have now become a diverse social space. As more non-traditional social groups enter into college campuses, homogenous characteristics of college-going population are gradually disappearing. Campuses are now occupied by a wide variety of students belonging to various social, economic, linguistic, gender, regional and physical ability backgrounds. Although it appears to be a positive development, existing research has raised concerns that social divisions and its associated practices, prejudices and values are getting reproduced in higher education campuses.
The research project attempts to understand the nature and forms of diversity in the campuses; and the structures and mechanisms that exist to deal with diversity and discrimination. The project also examines how the opportunity provided by the growing diversity can be better leveraged for inculcating civic and democratic learning and to transform the institutions which are assumed to have a crucial role to play in the contemporary society. The research will explore the nature and process by which HEI can be transformed to a secular social space where students acquire knowledge and skills to learn, work and live in an increasingly diverse and multi-cultural society.
The study adapts a combination of quantitative and qualitative methodology for collection and analysis of information. It involves questionnaire survey among the students, interview with faculty members, institutional leaders, faculty in-charge of various cells/committees and focus group discussions with students belonging to various socio-religious groups and gender.
The study is being implemented in institutions located across six states i.e., Bihar, Delhi, Karnataka, Kerala, Maharashtra and Uttar Pradesh. The institutions are Patna University and Patna College; Zakir Husain Delhi College, New Delhi (affiliated to Delhi University); National Institute of Technology, Surathkal, Karnataka; Sree Kerala Varma College, Thrissur (affiliated to the University of Calicut), Sree C Achutha Menon Government College, Thrissur (affiliated to the University of Calicut); RTM Nagpur University, Vasant Rao Naik Government Institute of Arts and Social Sciences, Nagpur; Institute of Science, Nagpur; RTM Nagpur University; Jai Narayan PG College, Lucknow; and Lucknow University. The preparation of the case study reports and national synthesis reports are in progress.
The project is funded by the ICSSR.
Project Coordinators/Principal Investigators: Dr. Nidhi S Sabharwal and Dr. Malish C M.
The rapid expansion of Indian higher education and diversification in terms of courses, providers and mode of delivery necessitates the understanding of the emerging governance and management structures which are more complex than before. The role of universities in expanding knowledge continues, while at the same time the institutional alternatives to them focus on skills’ development in areas linked directly to the market economy. The universities are becoming entrepreneurial. There is shift in resource allocation from an input-orientation to output and outcome-orientation. The diversified structure has made it imperative to study the governance and management structures to understand the changing role of the state, examine the issues of autonomy and accountability with measures to improve efficiency in operation, improve performance of institutions and staff and resource allocations, based on institutional performance.
The broad objectives of the research project are firstly to discuss the evolution of the governance structure and processes at the national, state and institutional level. The project also aims to understand how the Ministry of Education, Directorate of Higher Education, State Councils of Higher Education and higher education institutions interact. Further, the project will examine the role and functioning of governing bodies at universities and colleges. Finally, the project aims to study the management of higher education at the institutional level.
The research study explores how the governance and management of Indian higher education has evolved and also aims to understand the functioning of governance and management of higher education at the national and state level. The study also examines how higher education institutions are governed and managed. The study follows a descriptive and analytical research design and a comparative approach, analysing the similarities and differences in the governance and management in the selected institutions. The study has been launched in institutions from the following states: Banaras Hindu University in Uttar Pradesh, and state universities and their affiliated colleges i.e. Bharathiar University in Tamil Nadu University of Rajasthan in Rajasthan, and Savitribai Phule Pune University in Maharashtra.
Project Coordinator/Principal Investigator: Dr. Garima Malik
Teaching and learning is considered vital for all educational sectors. The landscape of higher education in India is continuously changing, with increased international competition, diverse student composition and types of educational service providers and increasing demand of value for money and efficiency. This calls for new teaching methods among other reform prerequisites. However, there seems a lack of substantial empirical evidence on the status of teaching and learning and development of higher education faculty in India.
This study intends to know how the teaching-learning process varies among disciplines and institutions and what measures are to be taken to improve teaching and learning in Indian higher education institutions. The study looks into faculty profiles, i.e. the social, academic and professional profile of the individuals teaching in Indian higher education institutions; perceptions of teachers about their roles, their articulation and understanding about teaching, their professional development needs and priorities; what transpires as teaching-learning and institutional support to the faculty in and out of the classroom to promote teaching-learning across disciplines; and students’ perception and assessment of the quality of teaching-learning experiences in their primary programs of study.
The specific objectives are to understand the process of teaching and learning in the higher education institutions (colleges and universities) in India and identify possible diversities and different practices; to understand the dynamics of teaching across a range of disciplines at bachelors’ and masters’ level programs; to analyse the effectiveness of teaching and institutional environment in the learning of the students in order to understand the policy priorities and policy responses in terms of teaching and learning, faculty and learner development in higher education.
The research project is a multi-state, multi-institutional study and employs mixed-methods’ approach to examine teaching and learning in various academic programs across the chosen set of higher education institutions (One University and one of its affiliated colleges) in five states. The Guru Ghasidas University, Chattisgarh; Calcutta University, West Bengal; Maharaja Sayajirao University of Baroda, Gujarat and Periyar University, Tamil Nadu are part of this project on Teaching and Learning in Indian Higehr Education.
Project Coordinator/Principal Investigator: Dr. Sayantan Mandal
The governments and individuals/households have been increasing their investment in higher education leading to massification of higher education in many countries. Committees and commissions on higher education in India have reflected on the need for institutions to seek resources in addition to the resource allocated from the government. The availability of resources at the institution level has been found to be inadequate to meet the growing demand for student enrolment. Consequently, many higher education institutions (HEI) have started cost-recovery measures, mostly in the form of levying higher rates of student fees and resource mobilisation strategies, with varying success.
There is a need to understand the resource allocation, patterns of utilisation of resources received in terms of grants as well as through income- generating activities in the Indian context. This study aims to map the diversified sources of funding of (HEI), to analyse adequacy or inadequacy of the resources, to understand the relative challenges in the mobilisation of additional resources by the diversified higher education institutions, to identify the activities that could not be carried out due to paucity of funds and to analyse the expenditure and utilisation pattern of the resources by the higher education institutions. The research methodology for the study is descriptive in nature, analysing secondary and primary data collected at the institutional level. The study attempts to find out about the different sources of funding of HEI; the utilisation pattern of the resources by the HEIs and the extent of resource gaps at the institutional level; activities affected by reduced resource availability and the strategies adopted by the institution to mobilise additional resources.
The study is based on the case studies of five states of the country representing five major zones of India i.e., Bihar, Odisha, Punjab, Uttarakhand and Telangana, the government departments that allocate fund to the respective higher education institutions, the universities located in these selected states and an affiliated college from each of the selected universities, and the SHECs that are operating in a few of these states. The study was launched with a workshop where all the research team members from B. R. Ambedkar Bihar University, Muzaffarpur, Bihar; Utkal University, Bhubaneswar, Odisha; Punjabi University, Patiala, Punjab; University of Hyderabad, Telangana; and Kumaun University, Uttarakhand participated.
Project Coordinator/Principal Investigator: Dr. Jinusha Panigrahi
The national assessment and accreditation council (NAAC), established in 1994, is responsible for setting of standards of higher education institutions in India as an external quality assurance (EQA)agency. Till recently, not many institutions have approached NAAC for accreditation. We do not have enough empirical evidence to say whether there has been any change in quality of the institutions that have approached NAAC. Quality assurance and role, nature and mandate of QA agencies, what they do and what they achieve, how it affects the institutions and whether the spending on the exercise of QA at the central/state and institutional level is worth it, can be addressed only by taking up a study in this area. The broad objectives of this research study are to understand how the EQA agencies impact the higher education institutions and programmes; to analyse the structure and function of IQA at the institutional level; to assess how EQA and IQA enhance quality at the institutional level. The research questions relate to the relationship between EQA system and IQA system, with focus on input, output and outcome; effect of EQA on the functioning of the University/affiliated college; organisation of IQA across selected subjects and interaction of IQA cells (IQAC) with departments; nature of feedback from IQA cells to the departments and colleges; effect of EQA on quality in terms of students’ learning.
This study follows a descriptive research design and interpretive approach, with substantial focus on interviews and questionnaire survey with faculty, administrators, and students; analysis of documents such as annual quality assurance reports, self-study reports submitted to NAAC, peer review reports of the institutions; analyses of student-related data maintained at the IQAC at the institutions.
Five universities in the 2nd or subsequent cycle of NAAC accreditation and an accredited college affiliated with each of the selected universities have been selected from five states. Three-member research teams in each state have been constituted, with faculty from each of the selected institutions. The study has been launched with the first research methodology workshop of the research teams from Mysore University, Karnataka; Devi Ahilya Vishwavidyalay, Madhya Pradesh; North Eastern Hill University (NEHU), Meghalaya; Mohanlal Sukhadia University, Rajasthan; and Osmania University, Telangana.
Project Coordinator/Principal Investigator: Dr. Anupam Pachauri
The problem of graduate employability has both supply and demand side aspects. Also the problem of employability and skills deficit cannot be completely delinked from the employment, unemployment and labour market conditions. Most studies look at one single aspect. In addition, massification and the experience of unemployment have challenged the Humboldtian idea of the research-oriented university and necessitated to look at the problem in a broader context of external as well as internal factors like general labour market conditions, local and global labour market demand at the macro level ;quality of education, possibilities for career counselling, provision of training courses, transition opportunities, Demand Supply Context at the institutional level; Effectuation factors like personal circumstances, willingness and preferences of individual employees as well as conditions and attitudes of employers.
The present study would try to fill this gap by combining both external and internal as well as demand and supply factors affecting and influencing graduate employability. The study proposes to understand the issue of Graduate Employability and Higher Education in India along three interlinked domain at the macro, institutional and individual levels:
- Macro Economic dimensions of Educated Employment/unemployment trends
- Changing Industry demands and Dimensions of University/ Higher Education
- Individual Stake holders’ changing perceptions/expectations regarding Higher education participation and provision in terms of employment readiness.
Against the backdrop of changing employment/unemployment scenario of the educated youth in India, the study shall seek to explore the following questions.
The study shall try to explore the above questions with a focus by generating perspectives of the major stakeholders - the employers and the new employees, students and teachers. The focus shall be to understand what is their awareness regarding the concept of “employability skills”, identify the types of employability skill gaps existing among the new job entrants , the differences existing therein by gender and social groups and the expectations of the employers from the universities in preparing industry ready graduates. The study shall also try to explore the challenges the new employees experience in their work place, to what extent they are required to supplement their university education with external trainings of different nature to fill in this gap.
Project Coordinator/Principal Investigator: Prof. Mona Khare
Research Paper Series
The CPRHE brings out a regular publication Series entitled CPRHE Research Papers. The purpose of this series is to disseminate the research carried out in the Centre and to continue a dialogue with researchers and policy-makers. These papers will be written by the CPRHE faculty members or research teams or prepared by others on the request of CPRHE.
- 21. Equity Policies in Higher Education in South Asia with Special Emphasis on India
- 20. The Role of Higher Education Institutions and Faculty Members in Higher Education Outreach in India
- 19. College Readiness and Student Success in Higher Education in India: An Inclusive Agenda
- 18. Governance and Management of Higher Education Institutions in India: An Empirical Analysis
- 17. Digital Technology Integration in Teaching and Learning in Indian Higher Education Influencing Factors, Policy Directions, and Government Initiatives
- 16. The Future of Higher Education in India From Massification to Universalisation
- 15. The Political Economy of Indian Higher Education: Understanding Systemic Challenges for Delhi
- 14. Graduate Employment and Sustainable Employability Skills in India
- 13. Fees in Private Higher Education Institutions: A Study of Deemed to be Universities in India
- 12. Equity and Inclusion in Higher Education in India
- 11. Concentration of Higher Education Institutions in India: A Regional Analysis
- 10. Student Diversity and Social Inclusion: An Empirical Analysis of Higher Education Institutions in India
- 9. Teaching-Learning in Higher Education: Evolution of Concepts and A New Tool of Analysis
- 8. Teacher Recruitment in Higher Education in India: An Analysis of National Eligibility Test (NET)
- 7. English as a Medium of Instruction in Indian Education: Inequality of Access to Educational Opportunities
- 6. Financing of Higher Education: Allocation of Resources to Public Higher Education Institutions in India and Other Innovative Methods of Financing
- 5. Governance and Management of Higher Education Institutions in India
- 4. Re-Imagining Indian Higher Education: A Social Ecology of Higher Education Institutions
- 3. Student Diversity and Civic Learning in Higher Education in India
- 2. Reforms in Higher Education in India: A Review of Recommendations of Commissions and Committees on Education
- 1. Challenges of Massification of Higher Education in India
Research Report Series
The CPRHE brings out a regular publication Series entitled CPRHE Research Papers. The purpose of this series is to disseminate the research carried out in the Centre and to continue a dialogue with researchers and policy-makers. These papers will be written by the CPRHE faculty members or research teams or prepared by others on the request of CPRHE.
- 1. Student Diversity and Social Inclusion: An Empirical Analysis of Higher Education Institutions in India
- 1.1 Diversity and Inclusion in Higher Education: A Study of Selected Institutions in Bihar
- 1.2 Diversity and Inclusion in Higher Education: A Study of Selected Institutions in Delhi
- 1.3 Diversity and Inclusion in Higher Education: A Study of Selected Institutions in Karnataka
- 1.4 Diversity and Inclusion in Higher Education: A Study of Selected Institutions in Kerala
- 1.5 Diversity and Inclusion in Higher Education: A Study of Selected Institutions in Maharashtra
- 1.6 Diversity and Inclusion in Higher Education: A Study of Selected Institutions in Uttar Pradesh
- 2.1 Governance and Management of Higher Education in India: A Study of Selected Institutions in Rajasthan
- 2.2 Governance and Management of Higher Education in India: A Study of Selected Institutions in Maharashtra
- 2.3 Governance and Management of Higher Education in India: A Study of Selected Institutions in Tamil Nadu
- 2.5 Governance and Management of Higher Education in India: A Study of Selected Institutions in Uttar Pradesh
CPRHE Policy Briefs
- CPRHE Policy Briefs 6 and 7 on Governance and Management of Higher Education [English]
- CPRHE Policy Briefs 6 and 7 on Governance and Management of Higher Education [Hindi]
- CPRHE Policy Briefs 4 and 5 on Financing of Higher Education [English]
- CPRHE Policy Briefs 4 and 5 on Financing of Higher Education[Hindi]
- CPRHE Policy Briefs 1,2 and 3 on Diversity and Inclusion in Higher Education [English]
- CPRHE Policy Briefs 1,2 and 3 on Diversity and Inclusion in Higher Education [Hindi]
International and National Seminar Reports
- Report on the International Seminar on Diversity and Inclusion in Higher Education, 2023
- Report on the International Seminar on Governance and Autonomy in Higher Education, 2020
- Report on the International Seminar on Employment and Employability of Higher Education Graduates, 2019
- Report on the International Seminar on Quality and Excellence in Higher Education, 2018
- Report on the National Seminar on Student Diversity and Discrimination in Higher Education in India, 2017
- Report on the International Seminar on Innovations in Financing of Higher Education, 2017
- Report on the International Seminar on Teaching-Learning and New Technologies in Higher Education, 2016
- Report on the International Seminar on the Massification of Higher Education in Large Academic Systems, 2014
CPRHE State Higher Education Council Reports
- A Report of the Consultative Meeting on State Higher Education Council (SHEC), 2023
- A Report of the Consultative Meeting on State Higher Education Council (SHEC), 2022
- A Report of the Consultative Meeting on State Higher Education Council (SHEC), 2021
- A Report of the Consultative Meeting on State Higher Education Council (SHEC), 2019
- A Report of the Consultative Meeting on State Higher Education Council (SHEC), 2018
CPRHE Research at Glance
Faculty & Staff

Director
pkmisra[at]niepa[dot]ac[dot]in
Prof. Pradeep Kumar Misra
Prof. Pradeep Kumar Misra, a Professor and Director of the Centre for Policy Research in Higher Education (CPRHE) at the National Institute of Educational Planning and Administration (NIEPA), New Delhi, has made significant contributions to the fields of higher education, educational technology, and teacher education.
His academic journey is marked by several prestigious international research scholarships, highlighting his global recognition. These include the Fulbright-Nehru Academic and Professional Excellence Fellowship, the Commonwealth Academic Fellowship, DAAD Doctoral and Senior Researcher Scholarships, the Erasmus Mundus Visiting Scholar Scholarship, the National Scholarship of the Slovak Republic, the MASHAV Scholarship from the Israeli Government, and the Research Exchange Scholarship from FMSH in France. Additionally, he has received a Joint Research Project grant under the ICSSR (India) and NIHSS (South Africa). He is also an active member of the academic bodies of various institutions and organizations both in India and abroad.
Prof. Misra has published extensively both nationally and internationally, completed research and development projects, and developed educational media programs. His recent books, Teaching Competencies for 21st Century Teachers: Practical Approaches to Learning (Routledge, 2024) and Learning and Teaching for Teachers (Springer, 2021), are not just publications but prime examples of his impactful work that resonates with teachers globally. His recent books include Case Studies on Blended Learning in Higher Education: Design, Development, and Delivery (Springer, 2025), India Higher Education Report 2023: Higher Education Research (Routledge, 2025), and Case Studies on Blended Learning in Higher Education: Policy, Planning and Quality Assurance (Springer, 2024).
Prof. Misra has also developed educational media programs and supervised Ph.D. scholars. His extensive experience in education has taken him to many countries, spanning continents and cultures.
CPRHE Research at Glance
Screen Reader Access
| Screen Reader | Website | Free / Commercial |
|---|---|---|
| Non Visual Desktop Access (NVDA) | http://www.nvda-project.org(External website that opens in a new window) | Free |
| System Access To Go | http://www.satogo.com/(External website that opens in a new window) | Free |
| Web Anywhere | http://webanywhere.cs.washington.edu/wa.php(External website that opens in a new window) | Free |
| Hal | http://www.yourdolphin.co.uk/productdetail.asp?id=5(External website that opens in a new window) | Commercial |
| JAWS | http://www.freedomscientific.com/jaws-hq.asp(External website that opens in a new window) | Commercial |
| Supernova | http://www.yourdolphin.co.uk/productdetail.asp?id=1(External website that opens in a new window) | Commercial |
| Window-Eyes | http://www.gwmicro.com/Window-Eyes/(External website that opens in a new window) | Commercial |
Recent Events
- Second Research Methodology Workshop on Widening Access to Higher Education in India: Institutional Approaches to be held on 17-18 September, 2024
- Second Research Advisory Committee Meeting on Widening Access to Higher Education in India: Institutional Approaches to be held on 28 August 2024, New Delhi (Online)
- First Peer Review Meeting on IHER 2025: Multidisciplinary Higher Education on 02 August, 2024 (Online)
- Executive Committee Meeting on March 06, 2024 (Online)
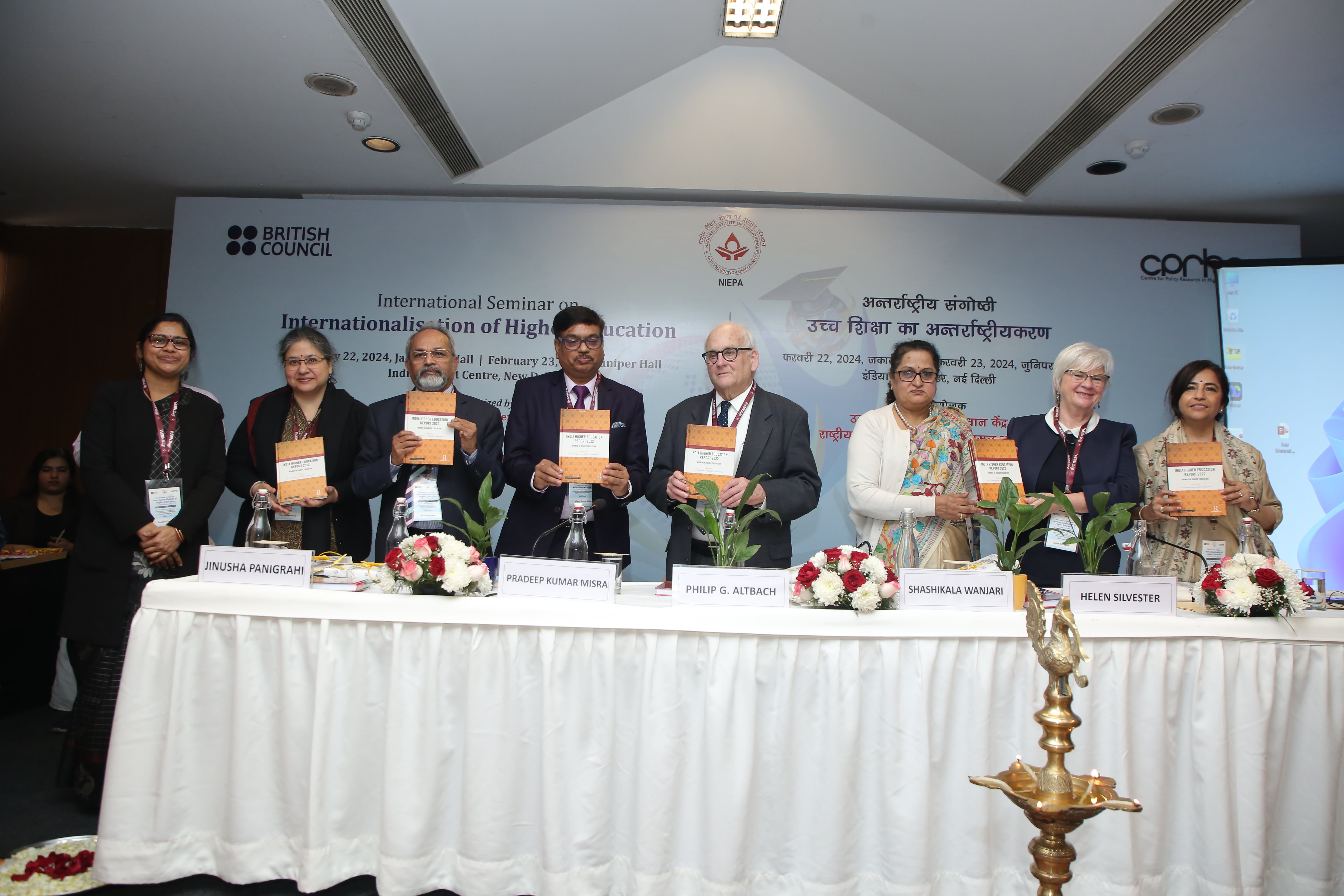
- International Seminar on Internationalisation of Higher Education on 22-23 February, 2024
- Policy Dialogue Webinar on Reforms for Institutional Governance of Higher Education on 09 February 2024
- First Methodology Workshop on 'Integrating Digital Technology with Teaching and Learning in Indian Higher Education to be held on January 22-23 2024
- First Methodology Workshop on Widening Access to Higher Education in India: Institutional Approaches held on November 16 - 17 2023 at 9:00hrs
- Second Research Methodology Workshop on Project "College Readiness and Student Success in Higher Education in India on 18-19 October, 2023
- Second Research Expert Committee Meeting on College Readiness and Student Success in Higher Education October 4, 2023
- IHER 2024: Second Peer Review Meeting on Technology and Higher Education on 27 September 2023 at 09:30 (Online Gmeet)
- Consultative Meeting on Modules on Student Diversity with Directors of HRDC on 5-6 September, 2023 (Unscheduled)
- Expert Group Meeting on Two Policy Briefs on Governance and Management of Higher Education in India (Online)
- First Expert Committee Meeting on New Managerialism: The Changing Management of Public Higher Education Institutions in India (Online)
- First Expert Committee Meeting on Financing of Technical and Professional Education: A Comparative Study of Public & Private Higher Education Institutions (Online)
- Policy Dialogue Webinar on Reforms for Institutional Financing of Higher Education
- Instrument Development Meeting:on Integrating Digital Technology with Teaching and Learning in Indian Higher Education
- Two Day Consultative Meeting on the State Higher Education Councils on 16 and 17 March, 2023
- CPRHE/NIEPA Executive Committee Meeting on March 3, 2023
- International Seminar on Diversity and Inclusion in Higher Education on 16 and 17 February 2023 in New Delhi
- G20 Consultative Committee Meeting on Tech-Enabled Learning on February 13, 2023 (NIEPA)
- The Expert Group Meeting on CPRHE Policy Briefs, Financing of Higher Education: Institutional Responses to Decline in Public Funding, scheduled on 17, November 2022 (Online)
- First Research Methodology Workshop on College Readiness and Student Success on 09-10 November 2022
- First Advisory Committee Meeting on Widening Access to Higher Education in India: Institutional Approaches scheduled on 20 October, 2022 (Online)
- IHER 2023 :Second Peer Review Meeting on Research in Higher Education in India scheduled on 19 October, 2022 (Online)
- First Research Expert Committee Meeting on "Integrating Digital Technology with Teaching and Learning in Indian Higher Education (Online)
- IHER 2023 : First Peer Review Meeting on Research in Higher Education in India
- Webinar on A Fair Chance for Education: Gendered Pathways to HE Access and Choice
- Interactive Session with visiting team from the University of Warwick, UK
- Third Expert Group Meeting on Quality of Higher Education in India: A Study of External and Internal Quality Assurance at the Institutional Level
- Two Day Consultative Meeting, Online on State Higher Education Council (SHEC) on 16 and 17 March, 2022
- Executive Committee Meeting, Online on 02 March, 2022 at 11.00 hrs
- Instrument Development Meeting on College Readiness and Student Success in Higher Education in India
- Webinar on Financing Higher Education jointly organised by NIEPA and AIU
- Expert Group Meeting on Modules on Managing Student Diversity in Higher Education scheduled on 24 November, 2021
- Second Peer Review Meeting on Women in Higher Education
- Webinar on Research, Innovation and Ranking in Higher Education
- Webinar on Knowledge Pluralism and Linguistic and Cultural Diversity in Higher Education
- First Research Expert Committee Meeting on College Readiness and Student Success in Higher Education in India
- First Peer Review Meeting: India Higher Education Report 2022 on "Women in Higher Education"
- Expert Group Meeting on "Higher Education Success and Social Mobility: A Study on Coaching Schemes for SC/ST/OBC and Minorities in Universities and Colleges" on 16 April 2021
- State Higher Education Council Meeting on 18 and 19, March 2021
- CPRHE, Executive Committee Meeting on 12, March 2021
- Second Peer Review Meeting on “India Higher Education Report 2021 on Private Higher Education
- Policy Dialogue Webinar on Reforms for Diversity and Inclusion in Higher Education Institutions
- Webinar on Flexible Learning Pathways: Challenges and Opportunities for Higher Education in India
- First Peer Review Meeting on India Higher Education Report 2021 on Google Meet
- Webinar on Advancing Gender Equity and Women Empowerment through Education
- CPRHE, Executive Committee Meeting held on 26 February 2020
- International Seminar on Governance and Autonomy in Higher Education on 20 and 21 February 2020
- Meeting with a Group of 24 Students from New York University Meeting on 23 January 2020
- Nordic-India Higher Education Summit on Internationalisation for Improving Access, Equity and Sustainability in Higher Education
- Second Peer Review Meeting on India Higher Education Report 2020
- First Peer Review Meeting on India Higher Education Report 2020
- CPRHE, Executive Committee Meeting on 27 March 2019
- State Higher Education Council Meeting on 25-26 Feb 2019
- International Seminar on “Employment and Employability of Higher Education Graduates” on 19 and 20 February 2019
- IHER 2019 Second Peer Review Meeting on Governance and Management of Higher Education in India
- Third Expert Committee Meeting on the Research Project “Teaching and Learning in Indian Higher Education”
- Third Expert Committee Meeting on "Governance and Management of Higher Education Institutions in India"
- Third Expert Committee Meeting on “Financing of Public Higher Education Institutions in India"
- IHER 2019, First Peer Review Meeting on Governance and Management of Higher Education in India
- Executive Committee Meeting on 13 March 2018
- International Seminar on “Quality and Excellence in Higher Education” on 22 and 23 February 2018
- Two Day Consultative Meeting on the State Higher Education Councils 15 and 16, February 2018
- CPRHE, NIEPA with University of Massachusetts, Amherst Meeting on Student Diversity and Social Inclusion in Higher Education was organised in NIEPA, New Delhi on 13 February, 2018.
- The Third Research Methodology Workshop on Financing of Public Higher Education Institutions in India: A Study of Flow of Funds and their Utilisation was held on 25-26 September, 2017
- The second Peer-Review Workshop on IHER 2018 on ‘Financing of Higher Education’ was organised on 14, September 2017
- The Third Research Methodology Workshop for the Research Project Governance and Management of Higher Education in India was held on September 11-12, 2017
- Third Research Methodology Workshop on the Research Project, Quality of Higher Education in India: A Study of External and Internal Quality Assurance at the Institutional Level, held on 6-7 September, 2017
- Third research methodology workshop on the research project Teaching and Learning in Indian Higher Education was organised on 29-30 August, 2017
- The Expert Group Meeting on CPRHE Policy Briefs, Diversity and Inclusion in Higher Education, held on 20, June 2017
- First Peer Review Workshop on IHER 2018 on ‘Financing of Higher Education’ was organised on 30 May, 2017
- First Research Methodology Workshop for the Research Project Higher Education Success and Social Mobility: A Study on Coaching Schemes for SC/ST/OBC and Minorities in Universities and Colleges was held on 2-3 May, 2017
- National Seminar on “Diversity and Discrimination in Higher Education” on 27 and 28 February 2017
- International Seminar on “Innovations in Financing of Higher Education” on 16 and 17 February 2017
- First Methodology Workshop for the CPRHE Research Study on " Employability of Higher Education Graduates" held on 18-19 January 2017
- Expert Group Meeting on Modules for Managing Student Diversity in Higher Education held on 17 January 2017
- Expert Group Meeting on Modules for Managing Student Diversity in Higher Education held on 17 January 2017
- The Research Instrument Development Workshop for the research project, “Higher Education Success and Social Mobility: A Study on UGC Coaching Schemes for SC/ST/OBC and Minorities in Universities and Colleges” held on 22 December 2016.
- The Expert Committee Meeting of the research project on “Employability of Higher Education Graduates in India” held on 26 October 2016
- Research Advisory Committee meeting to discuss the synthesis report of the research project on “Higher Education for Civic Learning & Democratic Engagement: A Study of Diversity and Discrimination in Higher Education Institutions” held on 18 October 2016
- The Research Advisory Committee meeting of the project on “Higher Education Success and Social Mobility: A Study on UGC Coaching Schemes for SC/ST/OBC and Minorities in Universities and Colleges” held on 4 October 2016
- The Peer Review Meeting to discuss the draft chapters of the India Higher Education Report 2017 held on 27 September 2016
- The Peer Review Meeting to discuss the framework and individual chapters of the India Higher Education Report 2017 on Quality and Teaching Learning in Higher Education in India held on 23 June 2016
- Research Methodology Workshop to discuss draft reports of state teams for research project on “Diversity and Discrimination in Higher Education: A Study of Institutions in Selected States of India” held on 7-8 June 2016
- Research Instruments Development Workshop of the research project on “Employability of Higher Education Graduates in India”, 12 May 2016.
- The Research Methodology/Analysis Framework Workshop on “Financing of Public Higher Education Institutions in India: A Study of Flow of Funds and their Utilisation”, 18-19 April 2016
- Research Methodology Analysis Framework Workshop on “Governance and Management of Higher Education" held on 11-12 April 2016
- Expert Committee Meeting for the research project on “Governance and Management of Higher Education” held on 08 April 2016
- Executive Committee Meeting
- International Seminar on Teaching-Learning and New Technologies in Higher Education
- Research Methodology Workshops
- Interactive Session on Research and Policy in Higher Education
- Panel Discussion on Politics of Higher Education Policy and Reforms
- International Seminar on Massification of Higher Education in Large Academic Systems
- Expert Committee Meetings on Research
- State Higher Education Council (SHEC) Consultative Meeting
Contact Us:
National Institute of Educational Planning and Administration
Centre for Policy Research in Higher Education
17-B, Sri Aurobindo Marg,
New Delhi-110016 (INDIA),
Phone No:011 26544800,
Email Id: cprhe@niepa.ac.in